Hydrolab – Softening filtration
Hydrolab – Softening filtration

Water hardness is the sum of magnesium and calcium ions that occur in all possible combinations. Table 1 presents the main distribution of water hardness.
| General hardness by cations | General hardness by anions |
| carbonate hardness | non-carbonate hardness | |
| calcium hardness | Ca(HCO3)2, Ca(OH)2, CaCO3 | CaSO4, CaCl2, Ca(NO3)2 |
| magnesium hardness | Mg(HCO3)2, Mg(OH)2, MgCO3 | MgSO4, MgCl2, Mg(NO3)2 |
Types of water hardness:
– calcium/magnesium hardness is caused by dissolved calcium/magnesium salts.
– carbonate (transient) hardness is associated with the presence of compounds in the form of calcium and magnesium hydroxides, bicarbonates and carbonates. After boiling, this part of the total hardness of the water disappears.
– non-carbonate hardness (permanent) is caused by the presence of mainly calcium and magnesium salts. Most often they are sulphates, which form difficult to remove gypsum stone, e.g. CaSO4 and chlorides[2].
Units:
| units | mmol/1 | mial/l | on | oang | ofranc | mg CaCO3/l |
| mmol/l | 1 | 2 | 5,61 | 7,02 | 10 | 100 |
| mval/l | 0,5 | 1 | 2,8 | 3,5 | 5 | 50 |
| on | 0,178 | 0,356 | 1 | 1,25 | 1,78 | 17,0 |
| oang | 0,143 | 0,286 | 0,8 | 1 | 1,43 | 14,0 |
| ofranc | 0,1 | 0,2 | 0,56 | 0,7 | 1 | 1 |
| mg CaCO3/l | 0,01 | 0,02 | 0,056 | 0,07 | 0,1 | 1 |
According to the Regulation of the Minister of Health, water hardness intended for human consumption must be in the range of 60-500 mg CaCO3/l3/l
Tab. 3 Classification of waters according to general hardness [2].
| water | mg CaCO3 |
| very soft | 100-200 |
| soft | 100-200 |
| medium soft | 200-350 |
| hard | 350-550 |
| very hard | >550 |
Water softening is the removal of ions that are responsible for the hardness of water by passing water through sodium cation. When water flows through the ion exchange resin, calcium (Ca2+) and magnesium (Mg2+) ions are exchanged for sodium (Na+) ions.
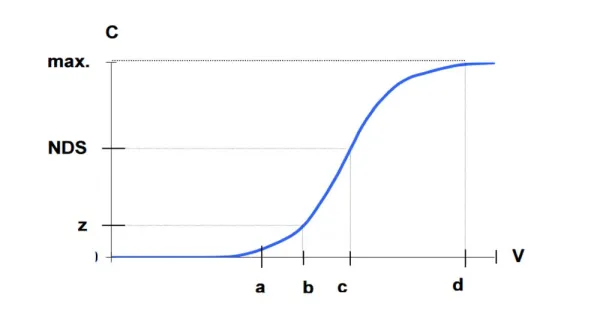
The length of the ion exchanger depends primarily on: – working exchange capacity of ion exchanger, – the amount of exchanged ions, – bed preparation for ion exchange. The ion exchange process lasts until the “bed breakthrough”, i.e. reaching the assumed concentration of ion exchanged in the purified solution (Fig. 1) [3].